10.2 - Relational Databases
Relational databases are one of the most common types of databases. They organize data into tables, which consist of rows and columns. Some fundamental concepts are listed below:
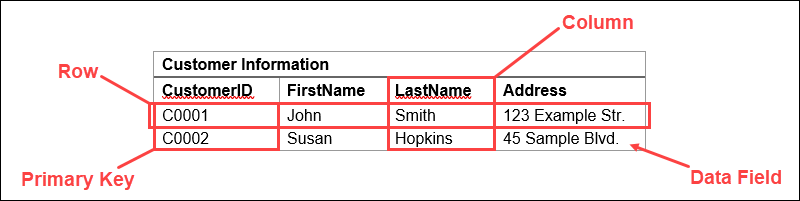
Table
- Definition: A table is a collection of related data entries that consists of columns and rows.
- Example: A
Customerstable with columns forCustomerID,Name,Email.
Row
- Definition: A row, also known as a record or tuple, represents a single data item in a table.
- Example: A row in the
Customerstable with data:1, John Doe, john@example.com.
Column
- Definition: A column, also known as a field or attribute, represents a data attribute within a table.
- Example: The
Emailcolumn in theCustomerstable.
Primary Key
- Definition: A primary key is a unique identifier for a record in a table.
- Example:
CustomerIDin theCustomerstable.
Foreign Key
- Definition: A foreign key is a column that creates a relationship between two tables.
- Example:
BuyerIDin theOrderstable might be a foreign key linking to theCustomerIDin theCustomerstable.
Relationships
- Relationships describe how tables are linked to each other.
- Cardinality refers to the numerical relationship between two entities. It specifies the number of instances of one entity that can be associated with an instance of another entity.
- Relationship Types:
- One-to-One
- One-to-Many
- Many-to-Many
- Self-Relationship